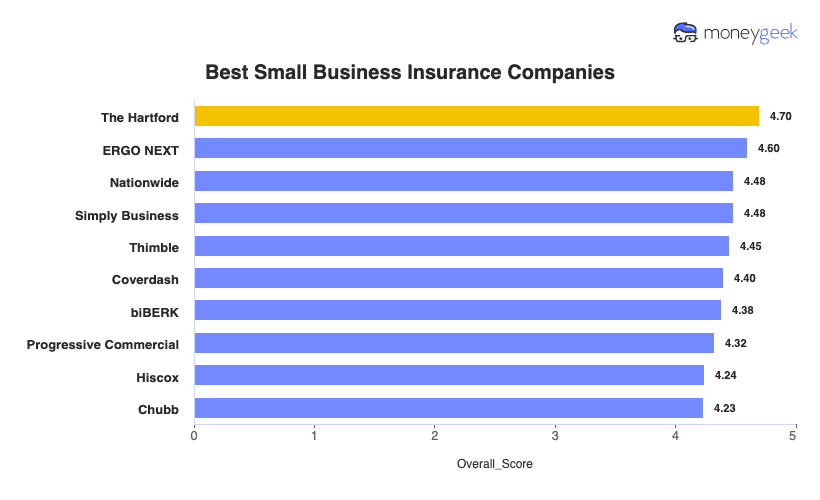
Below we have summarized which business insurance companies ranked at the top for each of our rating categories (Click each category to learn more about the winners).
Best By Rating Category:
- Best Cheap Small Business Insurance Overall: The Hartford
- Best Small Business Insurance Customer Experience: ERGO NEXT
- Best Small Business Insurance Coverage Options: Simply Business
Best By Coverage Type:
- Best General Liability Insurance: The Hartford
- Best Workers' Comp Insurance: ERGO NEXT and The Hartford tie
- Best Professional Liability Insurance: ERGO NEXT
- Best BOP Insurance: The Hartford
- Best Commercial Auto Insurance: ERGO NEXT
You can also click industry and state to learn more about the best companies at the factor level.
To ensure you make the most informed business insurance decision, we've also answered frequently asked questions related to picking the best company that you need to know.